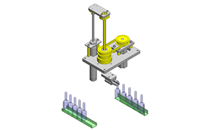
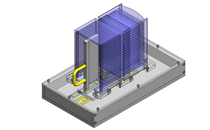
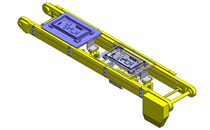
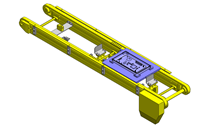
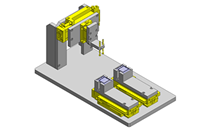
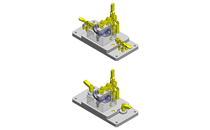
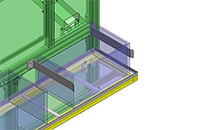
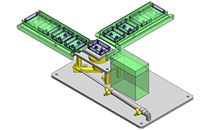
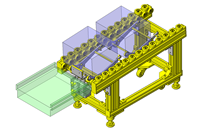
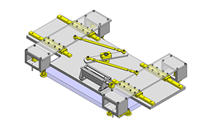
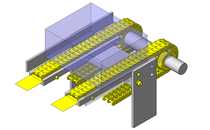
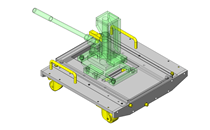
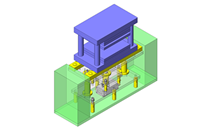
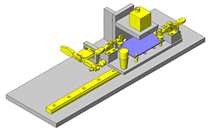
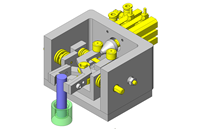
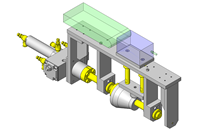
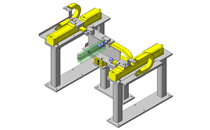
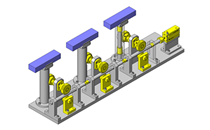
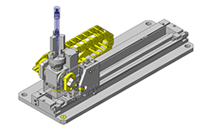
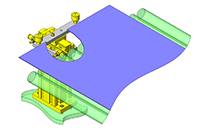
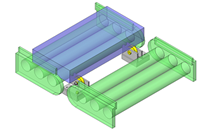
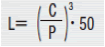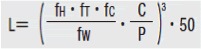Compact Cylinders
| Product name | Compact Cylinders |
| Part number | MSCCN20-50 |
* Orange colored cells in the table below indicate the part numbers used in this example.
Selection criteria
Effective for building a small-sized linear motion system
Back to page top
Available sizes
■Compact Cylinders
Tube
I.D. | External
Size | Rod Tip Screw | Stroke St | Body Length
(+ St shown below) | Rod Tip
Length |
| Screw Type | Dia. -
Pitch |
| 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 35 | 40 | 45 | 50 | 75 | 100 |
| φ12 | □25 | Tapped | M3×0.5 | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | − | − | − | − | − | − | 22 | 3.5 |
| φ16 | □29 | M4×0.7 | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| φ20 | □36 | M5×0.8 | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | − | − | 29.5 | 4.5 |
| φ25 | □40 | M6×1.0 | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | − | − | 32.5 | 5 |
| φ32 | □45 | M8×1.25 | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | − | − | 33 | 7 |
| φ40 | □52 | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | 39.5 |
| φ50 | □64 | M10×1.5 | − | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | 40.5 | 8 |
| φ63 | □77 | − | − | − | − | − | ○ | − | − | − | ○ | ○ | ○ | 46 |
| φ12 | □25 | Threaded | M5×0.8 | − | ○ | − | ○ | − | ○ | − | − | − | − | − | − | 22 | 14 |
| φ16 | □29 | M6×1.0 | − | ○ | − | ○ | − | ○ | − | − | − | − | − | − | 15.5 |
| φ20 | □36 | M8×1.25 | − | ○ | − | − | − | ○ | − | − | − | ○ | − | − | 29.5 | 18.5 |
| φ25 | □40 | M10×1.25 | − | ○ | − | − | − | ○ | − | − | − | ○ | − | − | 32.5 | 22.5 |
| φ32 | □45 | M14×1.5 | − | ○ | − | − | − | ○ | − | − | − | ○ | − | − | 33 | 28.5 |
| φ40 | □52 | − | ○ | − | − | − | ○ | − | − | − | ○ | − | ○ | 39.5 |
| φ50 | □64 | M18×1.5 | − | ○ | − | − | − | ○ | − | − | − | ○ | ○ | ○ | 40.5 | 33.5 |
| φ63 | □77 | − | − | − | − | − | ○ | − | − | − | ○ | ○ | ○ | 46 |
* Sensors are sold separately
Back to page top
Selection steps
■Selection procedure of compact cylinders (See "Technical Information" shown below for details.)
1. Define various conditions of the load
↓
2. Calculate cylinder output (In case of double acting type)
↓
3. Determine the tube I.D.
↓
4. Determine the theoretical reference speed
↓
5. Verify the cylinder's cushion mechanism
↓
6.Verify the lateral load applicable to the cylinder
Back to page top
Performance info.
■Load Information of Compact Cylinders
Min. Operating Pressure: 0.1 MPa
Max. Operating Pressure: 1.0 MPa
Theoretical Output (N) :
| Tube I.D. | Operation
Direction | Operating Pressure (MPa) |
| 0.4 | 0.5 |
| φ12 | Outstroke | 45 | 57 |
| Instroke | 34 | 42 |
| φ16 | Outstroke | 80 | 101 |
| Instroke | 60 | 75 |
| φ20 | Outstroke | 126 | 157 |
| Instroke | 94 | 118 |
| φ25 | Outstroke | 196 | 245 |
| Instroke | 151 | 189 |
| φ32 | Outstroke | 322 | 402 |
| Instroke | 241 | 302 |
| φ40 | Outstroke | 503 | 628 |
| Instroke | 422 | 528 |
| φ50 | Outstroke | 785 | 982 |
| Instroke | 660 | 825 |
| φ63 | Outstroke | 1247 | 1559 |
| Instroke | 1121 | 1402 |
Back to page top
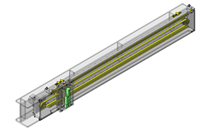
Miniature linear guide
| Product name | Miniature Linear Guide - Short Block |
| Part number | SE2BSZ10-115 |
| Features | Compliant with the industry standard specifications. 20% more compact than standard blocks. |
* Orange colored cells in the table below indicate the part numbers used in this example.
Selection criteria
Effective for building a small-sized linear motion system
Back to page top
Available sizes
■Miniature Linear Guide - Short Block
| Material | Hardness |
| Stainless Steel (440C Stainless Steel) | 56HRC- |
| Carbon steel (Alloy Steel including SCM) | 58HRC- |
■Sizes and Dimensions
| Number of Blocks | Block Width | Block Length | Overall Height | Rail Length |
| 1 | 17 | 19.6 | 8 | 40-130 |
| 20 | 22.9 | 10 | 35-275 |
| 27 | 27 | 13 | 45-470 |
| 32 | 32.7 | 16 | 70-670 |
| 2 | 17 | 19.6 x 2pcs. | 8 | 55-130 |
| 20 | 22.9 x 2pcs. | 10 | 75-275 |
| 27 | 27×2pcs. | 13 | 95-470 |
| 32 | 32.7×2pcs. | 16 | 110-670 |
* Please see the product pages for details of selectable sizes.
Back to page top
Selection Steps
■Miniature linear guide selection steps
- Determination on Operating Conditions
- (Moving mass, feed rate, motion pattern, life)
↓
- Temporary selection of linear guide specifications
- (Block type, overall height, rail length are temporarily selected according to the conditions of use.)
↓
- Basic safety check
-
- Allowable Load
- Operating Life
- Preload
Back to page top
Accuracy Info
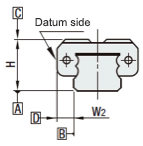
Preload and Accuracy Reference (Standard Blocks / Light Preload / High Grade)
(μm)
| Radial Clearance | -3~0 |
| H Dimension Tolerance | ±20 |
| Pair variation of H | 15 |
| Tolerance of dims. W2 | ±25 |
| Pair variation of W2 | 20 |
(μm)
| Rail Length(mm) |
| -80 | 81-200 | 201-250 | 251-400 | 401-500 | 501-630 | 631-700 |
| Running Parallelism | 3 | 7 | 9 | 11 | 12 | 13.5 | 14 |
Back to page top
Technical Calculations
Operating Life Calculation for Linear Guides
- Operating Life
- When the linear guide is loaded in linear reciprocating motion, scaly damages called flaking appear due to material fatigue as the stress works on the rolling elements (steel balls) and the rolling contact surfaces (rails) constantly. Total travel distance until the first flaking occurs is called the life of linear guides.
- Rated life
- Rated life is the total travel distance that 90% of linear guides of the same type can reach, under the same conditions, with no occurrence of flaking damage. Rated life can be calculated with the basic dynamic load rating and the actual load applied on the linear guides, as shown below.
-
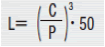
- Load must be calculated before actually using linear guides. To obtain loads during linear reciprocating motion, it is necessary to fully consider vibrations and impacts during motion as well as distribution condition of the load applied to linear guides. So, it is not easy to calculation the loads. Operating temperature also critically affects the life. Considering these conditions, the above-mentioned calculation formula will be as follows.
-
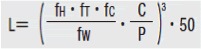
- L: Rated life (km)
- fH: Hardness Factor (See Fig-1)
- fT: Temperature Factor (See Fig-2)
- fC: Contact Factor (See Table-1)
- fW: Load Factor (See Table-2)
- C: Basic Dynamic Load Rating (N)
- P: Applicable load (N)
- Hardness factor (fH)
-
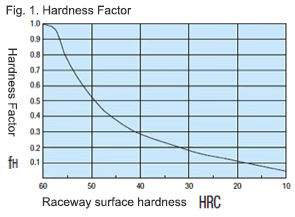
For liner guide applications, sufficient hardness is required for ball contact shafts. Inappropriate hardness causes less allowable load, resulting in shorter life.
Please correct the rated life with the hardness factor.
- Temperature factor (fT)
-
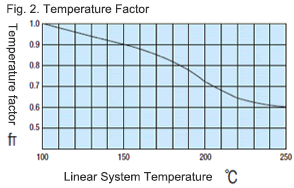
When the temperature of linear guides exceeds 100°C, the hardness of guides and shafts will be reduced, and the allowable loads will also be reduced compared to being used at room temperature, causing a reduction of life. Please correct the rated life by the temperature factor.
* Please use Linear Guides within the resistant temperature range shown on product pages.
- Contact factor (fC)
-
Table-1. Contact factor
Number of Blocks per Rail Contact Factor fC
| 1 | 1.00 |
| 2 | 0.81 |
| 3 | 0.72 |
| 4 | 0.66 |
| 5 | 0.61 |
For actual applications, more than two blocks are generally used per shaft. In this case, the load applied to each block varies depending on machining precision and is not uniformly distributed. As a result, per-block allowable load varies depending on the number of blocks per rail. Please compensate the rated life with contact factors on Table-1.
- Load factor (fW)
-
Table-2. Load factor
| Condition of Use | fw |
No shocks / vibrations,
low speed: 15 m/min. or less | 1.0-1.5 |
No significant shocks / vibrations,
medium speed: 60 m/min. or less | 1.5-20 |
With shocks / vibrations,
high speed: 60 m/min. or more | 2.0-3.5 |
To calculate load applied to the Linear Guides, in addition to object weight, it requires inertia force attributed to motion velocity or moment loads. However, it is difficult to calculation the load accurately due to potential vibrations and shocks caused by other element than repeated start-stop motions during reciprocating motion. Thus, Table-2 load factor helps simplify the life calculation.
- Applied Load P Calculation Method
- When moment load is applied to each block, convert the moment load into applied load by the following formula.
-
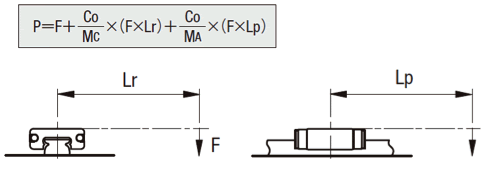
- P: Applicable Load (N)
- F: Downward load (N)
- C0: Static Load Rating (N)
- MA: Allowable Static Moment - Pitching Direction (N・m)
- MC: Allowable Static Moment - Rolling Direction (N・m)
- Lp: Load Point Distance (m) in Pitching Direction
- Lr: Load Point Distance (m) in Rolling Direction
Back to page top
Floating joint
| Product name | Floating Connectors - Extra Short Threaded Stud Mount |
| Part number | FJCMX5-0.8 |
| Features | Floating joints that can be used where there is little distance between cylinders and moving objects. |
* Orange colored cells in the table below indicate the part numbers used in this example.
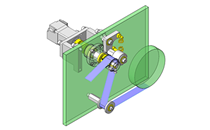
Selection criteria
Suitable for absorbing deviations in the radial direction.
Back to page top
Available sizes
■Floating Connectors - Extra Short Threaded Stud Mount
| Body / Cover | Joints | Spring | Washer |
| Material | Surface Treatment | Material | Surface Treatment | Hardness | Material | Material | Surface Treatment | Hardness |
| 1045 Carbon Steel | Black Oxide | 1045 Carbon Steel | Black Oxide | 35 - 45
HRC | 304 Stainless Steel−WPB | 304 Stainless Steel | Nitriding Treatment | 600HV - |
| 304 Stainless Steel | − | 440C Stainless Steel | − |
■Sizes
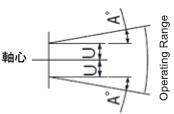
| Cylinder Mounting Side | Output Side | Allowable Misalignment
[U] | Allowable Angular Deviation
[A] | Body
Thickness | Body
Hex size | Overall Length |
| Screw Dia.-Pitch | thread length | Screw Dia.-Pitch | thread length |
| M5-0.8 | 6 | M8-1.25 | 8.5 | 0.5 | 4° | 14 | 24 | 33 |
| M6-1.0 |
| M8-1.25 | 8.5 | M10-1.5 | 10 | 15.5 | 27 | 39.5 |
| M10-1.5 | 10 | M14-2.0 | 11 | 19.5 | 30 | 47 |
<Allowable lateral misalignment U and allowable angular misalignment A>
Back to page top
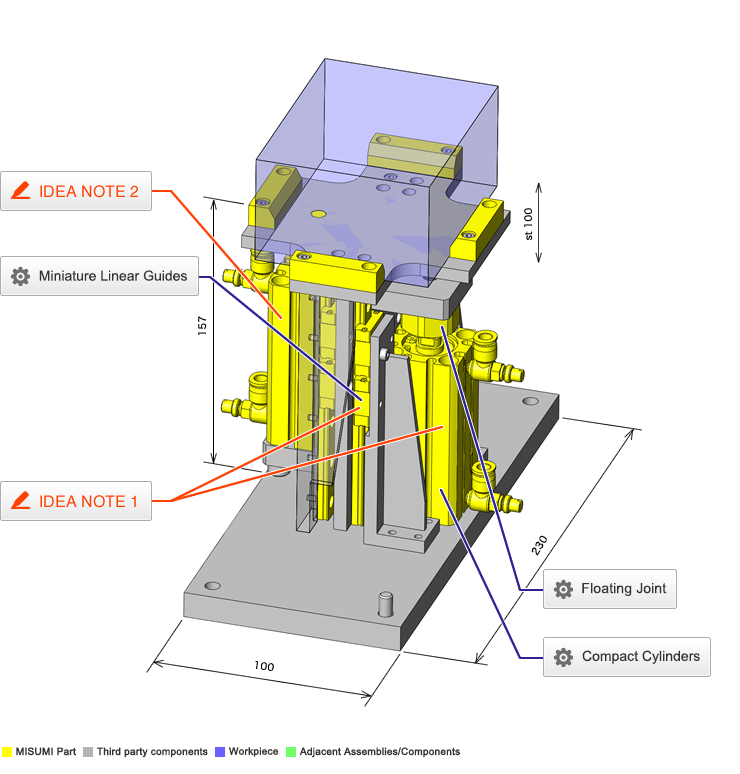
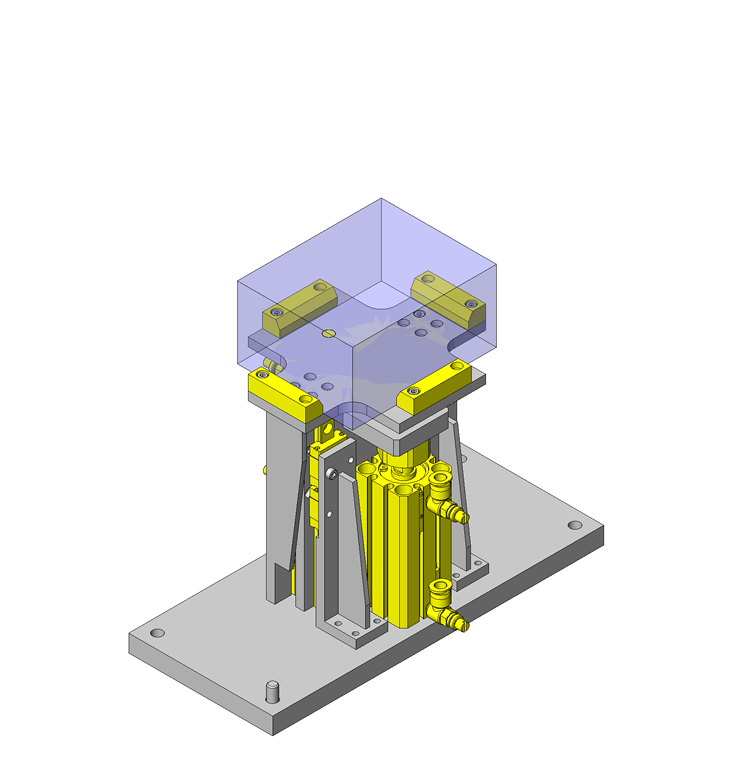
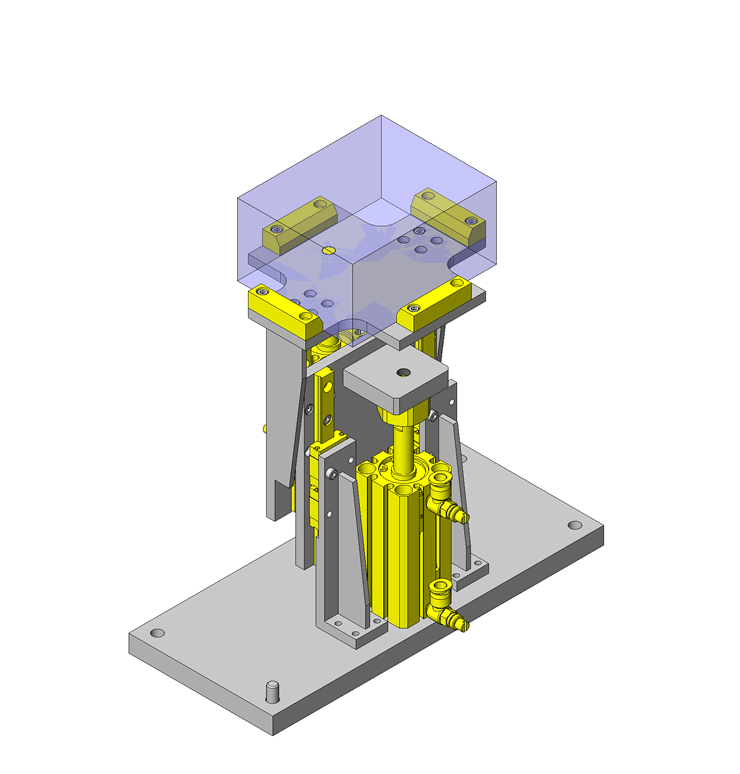
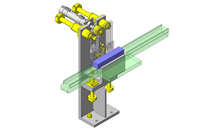
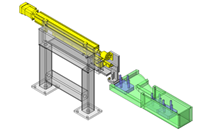
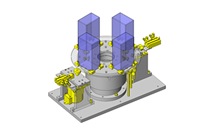
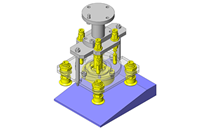
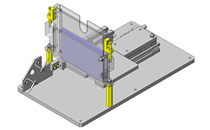
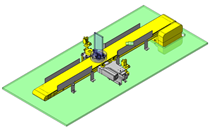
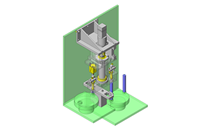
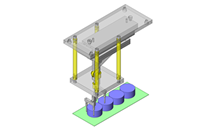
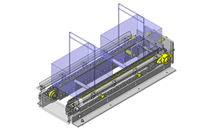
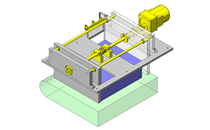
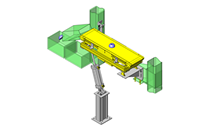
IDEA NOTE Air Cylinder and Linear Guide.
The first set of linear guides and air cylinder at as the first stage of lifting.
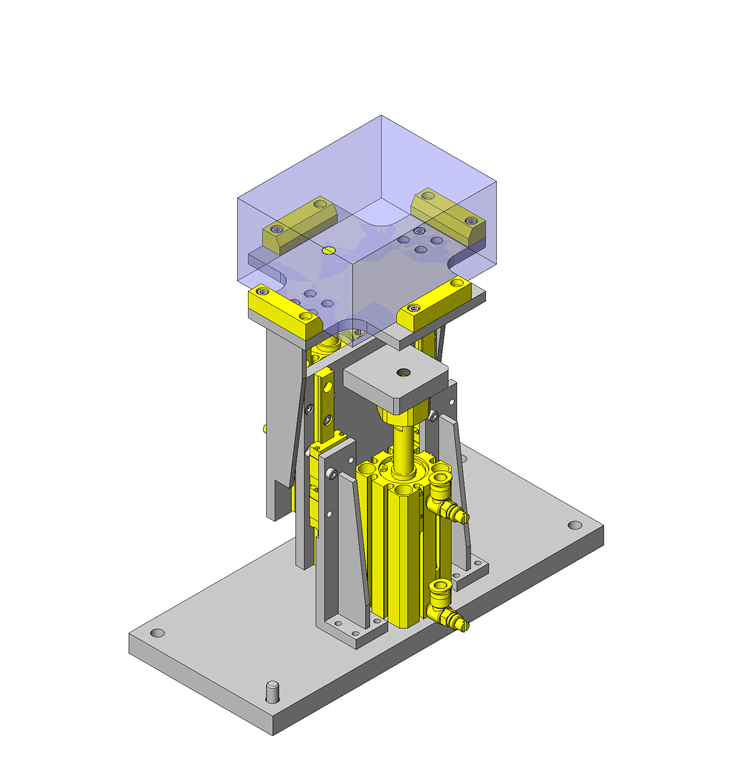
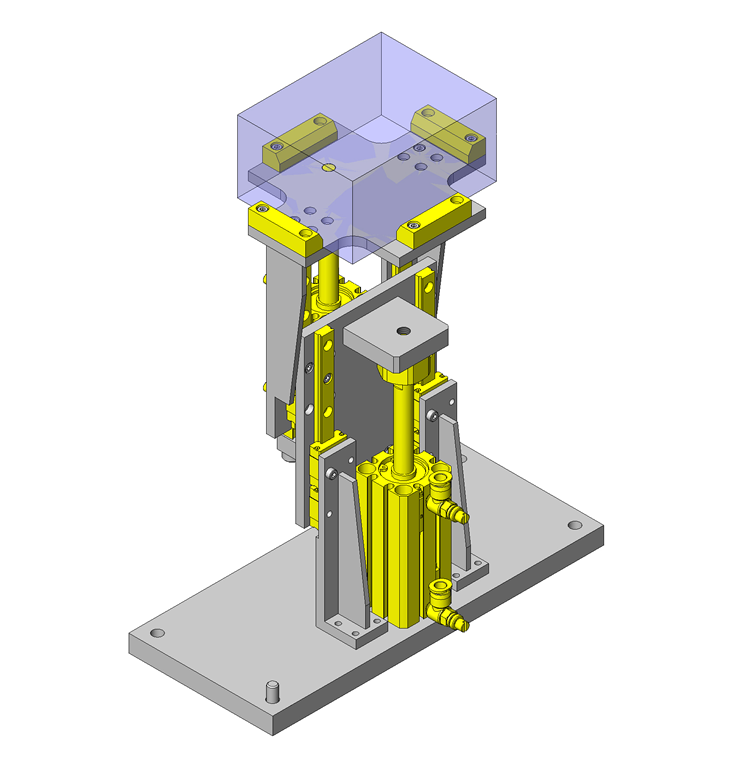
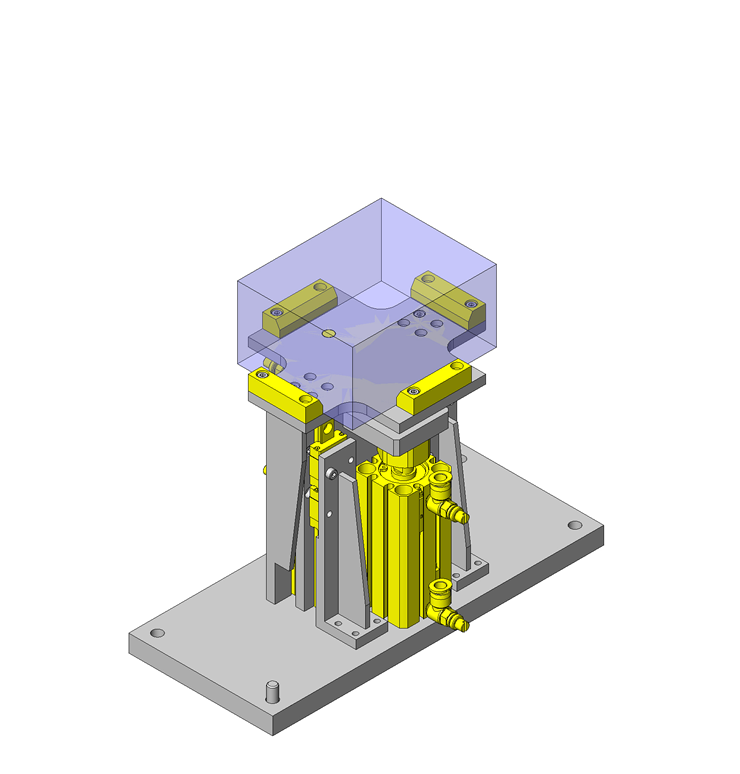
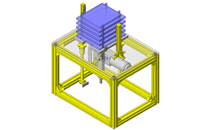
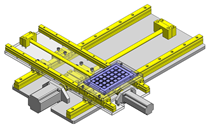
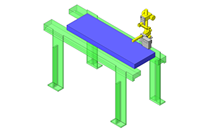
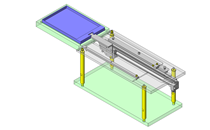
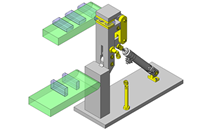
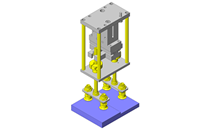
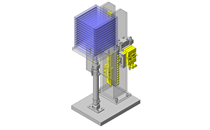
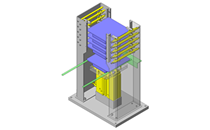
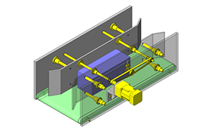
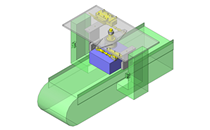
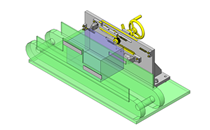
IDEA NOTE Increase Speed with Additional Cylinder and Linear Guides.
The additional set of linear guides and air cylinder act as second stage of vertical lifting mechanism for increased speed.